All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit Know AML.
The aml Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the aml Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The aml and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The AML Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Daiichi Sankyo, Johnson & Johnson, Syndax, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Kura Oncology, AbbVie, and has been supported through an educational grant from the Hippocrate Conference Institute, an association of the Servier Group.
Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View AML content recommended for you
The impact of concomitant ivosidenib on triazole levels in patients with AML or MDS
The IDH1 inhibitor ivosidenib, used in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), induces several cytochrome isoenzymes and is both a substrate and inhibitor of several transporter proteins. Patients diagnosed with AML are at an increased risk of invasive fungal infections and so are regularly recommended posaconazole and voriconazole therapy. These triazole therapies are also known to cause cytochrome enzyme inhibition and the use of these agents in combination with ivosidenib may result in a lower therapeutic efficacy.
Recently, Dinh et al.1 reported on the incidence of subtherapeutic triazole levels in patients with AML or myelodysplastic syndromes treated with concomitant ivosidenib in Cancer. We summarize the findings below.
Methods1
- This retrospective, single-center, cohort study included patients treated between March 4, 2016, and April 30, 2022.
- Subtherapeutic triazole levels were defined as posaconazole <700 ng/ml and voriconazole <1.0 μg/ml.
- Undetectable triazole levels were defined as posaconazole <50 ng/ml and voriconazole <0.1 μg/ml.
Key findings1
- N = 31
- All patients except one received 500 mg of ivosidenib once daily
- One patient initially received 250 mg once daily, but this dose was later increased to 500 mg once daily
- The median triazole levels were significantly lower in patients receiving concomitant vs non-concomitant ivosidenib (p < 0.05).
- Concomitant ivosidenib was associated with a higher frequency of subtherapeutic triazole levels vs non-concomitant ivosidenib (Figure 1).
Figure 1. The incidence rate of triazole levels considered subtherapeutic in patients who received concomitant and non-concomitant ivosidenib*
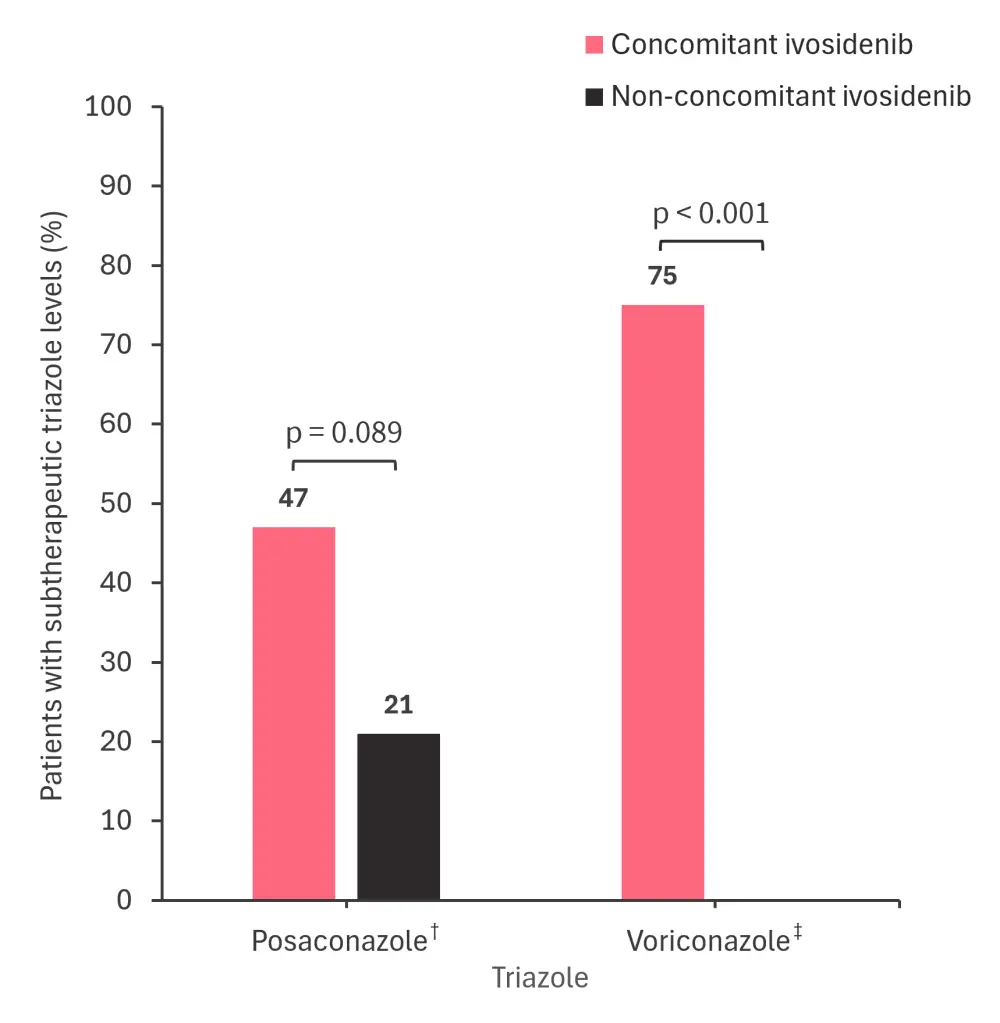
*Adapted from Dinh, et al.1
†Total posaconazole levels were measured in 43 patients treated with concomitant ivosidenib; total posaconazole levels were measured in 19 patients who did not receive concomitant ivosidenib.
‡Total voriconazole levels were measured in 36 patients treated with concomitant ivosidenib; total voriconazole levels were measured in six patients who did not receive concomitant ivosidenib.
- During ivosidenib therapy, posaconazole was undetectable in 5% of patients, and voriconazole in 31%.
- 16% of patients experienced a new invasive fungal infection during ivosidenib treatment
- 83% of these cases were in patients also receiving posaconazole
- 17% of these cases were also during receiving voriconazole
- All these patients had subtherapeutic triazole levels
- Overall, 16% of patients experienced Grade ≥3 QTc interval prolongation.
|
Key learnings |
|
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content


