All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit Know AML.
The aml Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the aml Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The aml and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The AML Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Daiichi Sankyo, Johnson & Johnson, Syndax, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Kura Oncology, AbbVie, and has been supported through an educational grant from the Hippocrate Conference Institute, an association of the Servier Group.
Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View AML content recommended for you
Latest updates on the QuANTUM-First study from ASH 2023
The randomized phase III QuANTUM-First trial (NCT02668653) evaluated the addition of quizartinib, a selective type II FLT3 inhibitor, vs placebo to standard chemotherapy and up to three years of continuation therapy in 539 patients aged 18–75 years with newly diagnosed FLT3-internal tandem duplication (ITD) mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML). The study design and results have been previously reported by the AML Hub, showing that the addition of quizartinib to intensive induction and consolidation chemotherapy is associated with an overall survival (OS) benefit compared with a placebo.1 These findings led to the approval of quizartinib by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the European Medicines Agency (EMA), and Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (MHLW) in this patient population.
During the 65th American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting and Exposition, several presentations discussed further analyses of this trial. Below, we summarize four presentations from Perl.1, Oliva.2, Erba.3, and Montesinos.4
Impact of measurable residual disease status on outcomes1
In this analysis, FLT3-ITD measurable residual disease (MRD) was assessed using a specifically designed polymerase chain reaction-next-generation sequencing assay. Of the 368 patients who achieved a composite complete remission (CRc), 321 had MRD data available (quizartinib arm, n = 162; placebo arm, n = 159).
Key findings
- In all patients, MRD negativity in both cutoffs of 1 × 10−4 (lowest level of quantitation) and 0 (undetectable) was associated with improved overall survival (OS) after induction, two cycles of consolidation, and the last consolidation cycle (Table 1).
Table 1. Impact of MRD status on survival outcomes in the QuANTUM-First study*
|
Therapy timepoint |
Median OS, months |
HR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|
|
MRD cutoff: 1 × 10−4 |
||
|
CRc after 1–2 cycles of induction |
||
|
MRD+ |
29.4 |
0.562 (0.398–0.794) |
|
MRD− |
NR |
|
|
CRc after 2 cycles of chemotherapy† |
||
|
MRD+ |
21.9 |
0.525 (0.376–0.731) |
|
MRD− |
NR |
|
|
After last consolidation cycle‡ |
||
|
MRD+ |
14.8 |
0.458 (0.332–0.633) |
|
MRD− |
NR |
|
|
MRD cutoff: 0 |
||
|
CRc after 1–2 cycles of induction |
||
|
MRD+ |
48.6 |
0.722 (0.450–1.159) |
|
MRD− |
NR |
|
|
CRc after 2 cycles of chemotherapy† |
||
|
MRD+ |
40.4 |
0.626 (0.419–0.935) |
|
MRD− |
NR |
|
|
After last consolidation cycle‡ |
||
|
MRD+ |
26.2 |
0.470 (0.334–0.661) |
|
MRD− |
NR |
|
|
CI, confidence interval; CRc, composite complete remission; HR, hazard ratio; MRD, measurable residual disease; NR, not reached; OS, overall survival. |
||
- Quizartinib was associated with deeper responses, with depth of remission increasing with the number of cycles (Table 2).
Table 2. Median FLT3-ITD VAF across treatment timepoints in the QuANTUM-First trial*
|
Median FLT3-ITD VAF, % |
Quizartinib |
Placebo |
p value |
|
CRc after 1–2 cycles of induction |
0.01 |
0.03 |
0.0251 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
CRc after 2 cycles of chemotherapy† |
0.0054 |
0.0171 |
0.0540 |
|
After last consolidation cycle‡ |
0 |
0.0017 |
0.0006 |
|
CRc, composite complete remission; FLT3, FMS‐like tyrosine kinase 3; ITD, internal tandem duplication; VAF, variant allele frequency. †Defined as either two cycles of induction or one cycle of induction and one cycle of consolidation. ‡Up to four cycles. |
|||
- There was a greater likelihood of having undetectable FLT3-ITD if treated with quizartinib vs placebo (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Patients with undetectable MRD (cutoff: 0) in each treatment phase of the QuANTUM-First trial
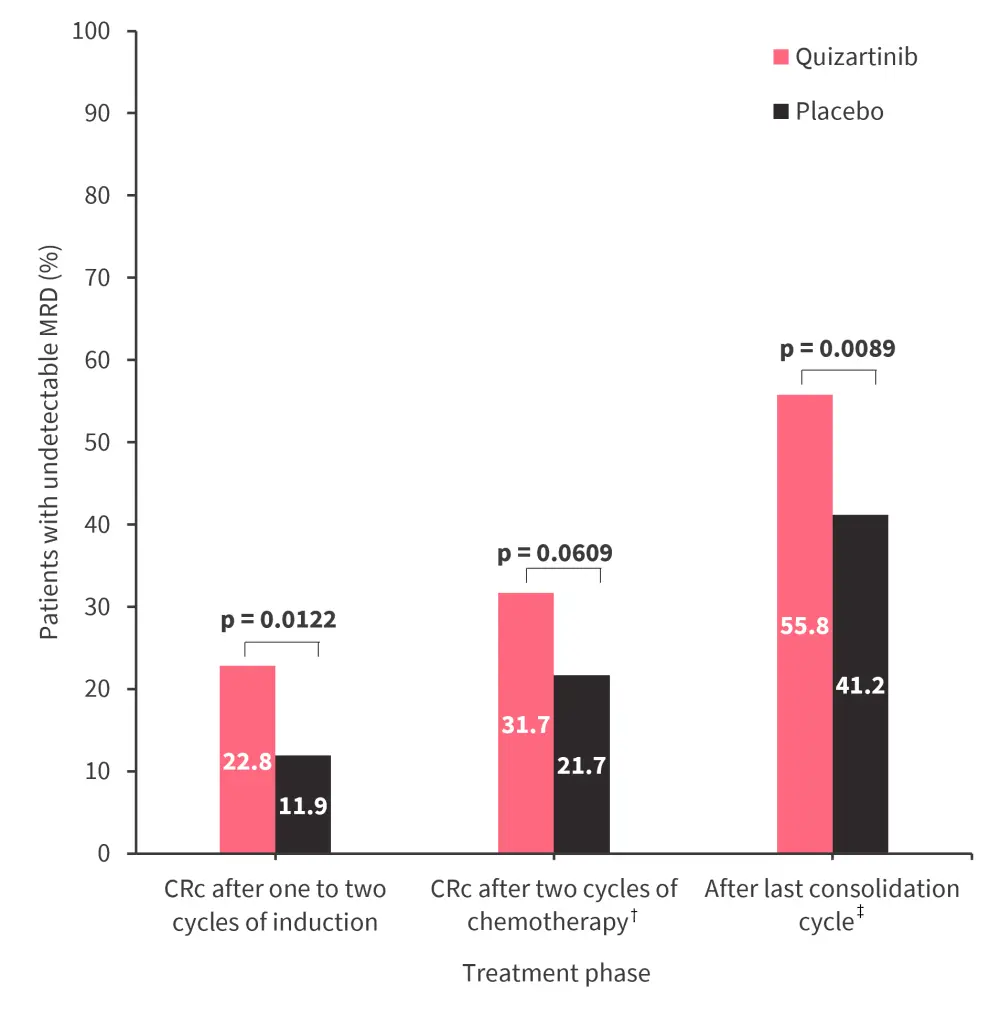
CRc, composite complete remission; MRD, measurable residual disease.
*Adapted from Perl.1
†Defined as either two cycles of induction or one cycle of induction and one cycle of consolidation.
‡Up to four cycles.
- Median OS was similar between treatment arms in patients who were MRD negative.
- In patients who were MRD positive, quizartinib was associated with a median OS benefit vs placebo after induction (median OS, not reached vs 35.4 months; hazard ratio [HR], 0.749; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.526–1.069), two cycles of chemotherapy (median OS, not reached vs 16.0 months; HR, 0.670; 95% CI, 0.465–0.967), and last consolidation cycle (median OS, 39.3 vs 14.8 months; HR, 0.725; 95% CI, 0.487–1.082).
Patient-reported outcomes2
Patient-reported outcomes (PRO) were measured using the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Core Quality of Life questionnaire (EORTC QLQ-C30). Baseline PRO measurements were assessed on Day 8 of induction Cycle 1, and the assessment was repeated on Day 28 of induction Cycles 1 and 2, Day 6 and Day 28 of consolidation Cycles 1–4, and Day 1 of every third continuation cycle (1–34). In total, PRO were measured in 509 patients (quizartinib arm, n = 254; placebo arm, n = 255).
Key findings
- This mixed model with repeated measures analysis showed improvements in global health status/QoL (quality of life), physical functioning, role functioning, social functioning, and emotional functioning scales in both the quizartinib and placebo arms, reaching a minimal clinically important difference of ≥10 points in each scale.
- No major changes over time in cognitive functioning scale scores were seen in either treatment arm.
- In the symptom subscales, improvements in minimal clinically important differences were observed in both treatment arms in fatigue, dyspnea, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, constipation, and appetite loss.
- Time until definitive deterioration was similar between the quizartinib and placebo arms across the functional and symptom subscales.
- Baseline scores for the global health status/QoL scale at the time of continuation therapy were high in both the quizartinib (mean, 67.5; standard deviation [SD], ±22.7) and placebo (mean, 71.0; SD, ±17.3) arms, relative to the normal European and U.S. populations, indicating improved QoL.
- The QoL improvement was maintained in both treatment arms over time.
Safety analysis by treatment phase and age3
This analysis reports the safety data from the QuANTUM-First trial by phase (induction, consolidation, continuation) and by age (<60, 60–75 years) in patients who received ≥1 dose of quizartinib or placebo.
Key findings
- Median adjusted treatment duration in the induction, consolidation, and continuation phase was 2 weeks (range, 0.1–4.0), 4 weeks (range, 0.3–8.0), and 1.3 years (0.4 weeks–3.1 years) in the quizartinib arm, respectively, and 2 weeks (0.3–4.0), 4 weeks (1.7–8.0), and 1.3 years (0.3 weeks–2.9 years) in the placebo arm, respectively.
- Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) of any-grade were similar between treatment arms through all treatment phases, although more Grade ≥3 TEAEs were observed in the quizartinib arm in the continuation phase (Table 3).
- TEAEs leading to discontinuation were more common in the quizartinib arm vs placebo in the induction phase (9.8% vs 4.1%), consolidation phase (5.8% vs 2.9%), and continuation phase (15.5% vs 7.6%).
- TEAEs of any-grade and Grade ≥3 was similar between treatment arms across both age groups (Table 3)
- TEAEs leading to death were higher in patients aged 60–75 years vs <60 years, but similar between treatment arms in both age groups.
- Rates of early death were higher in the quizartinib arm vs placebo arm across both age groups:
- infections were the most common TEAE leading to death for both age groups; and
- patients aged 60-75 years, but not <60 years, had a higher rate of death associated with infections and sepsis in the quizartinib vs placebo arm.
Table 3. TEAE observed by treatment phase and age group in the QuANTUM-First trial*
|
TEAE, % |
Induction |
Consolidation |
Continuation |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Quizartinib |
Placebo |
Quizartinib |
Placebo |
Quizartinib |
Placebo |
||
|
Any TEAE |
98.1 |
97.4 |
92.5 |
91.4 |
94.0 |
91.3 |
||
|
Grade ≥3 TEAE |
70.6 |
74.6 |
69.4 |
69.1 |
78.4 |
57.6 |
||
|
Serious TEAE |
28.3 |
24.6 |
34.1 |
30.9 |
33.6 |
37.0 |
||
|
AEs with fatal outcome |
7.2 |
4.9 |
4.6 |
2.9 |
2.6 |
7.6 |
||
|
TEAEs, % |
<60 years |
60–65 years |
||||||
|
|
Quizartinib |
Placebo |
Quizartinib |
Placebo |
||||
|
Any TEAE |
100.0 |
99.4 |
99.1 |
98.1 |
||||
|
Grade ≥3 TEAE |
91.2 |
88.8 |
93.4 |
90.7 |
||||
|
Serious TEAE |
52.8 |
40.0 |
55.7 |
54.6 |
||||
|
AE with fatal outcomes |
8.8 |
7.5 |
15.1 |
6.5 |
||||
|
TEAE, treatment-emergent adverse event. |
||||||||
Impact of duration of response on outcomes4
The impact of the duration of CR and CRc on OS was assessed using an extended Cox regression model with CR and CRc duration status as time-dependent variables. The impact of duration of CR on OS was also evaluated using a multistate model.
Key findings
- Among patients who achieved a CR, median OS was not reached (95% CI, 48.6 months–not estimable) in the quizartinib arm vs 35.4 months (95% CI, 15.1–not estimable) in the placebo arm (HR, 0.572; 95% CI, 0.400–0.816).
- In patients who did not achieve a CR, OS was similar between treatment arms (10.6 vs 9.6 months).
- In the extended Cox regression model, CR (HR, 0.156; 95% CI, 0.113–0.216; p <0.0001) and CRc (HR, 0.132; 95% CI, 0.098–0.177; p <0.0001) duration status was highly predictive of OS.
- Based on the multistate model, quizartinib was associated with a lower risk of relapse after the achievement of CR vs placebo (HR, 0.517; 95% CI, 0.331–0.807).
- Event-free survival (EFS) was similar between treatment arms in the primary analysis.
- When induction treatment failure was defined as not achieving a CR or CRc by the end of induction up to Day 56 from the last induction cycle, quizartinib was associated with an EFS benefit vs placebo (Table 4).
- 51 patients (quizartinib, n = 33; placebo, n = 18) achieved a CR between Day 42 and Day 56 of the last induction cycle.
Table 4. Analysis of EFS in the QuANTUM-First study by ITF definition*
|
ITF definition |
Median EFS (95% CI), months |
p value |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Quizartinib |
Placebo |
||
|
Primary analysis: no CR by Day 42 from start of last induction cycle |
0.03 (0.03–0.95) |
0.71 (0.03–3.42) |
0.2371 |
|
Sensitivity analysis: no CR by end of induction–Day 56 from start of the induction cycle |
5.0 (1.8–9.0) |
3.4 (1.7–5.5) |
0.0323 |
|
Sensitivity analysis: no CRc by end of induction–Day 56 from start of last induction cycle |
11.9 (8.1–16.5) |
5.7 (4.0–6.9) |
0.0031 |
|
CI, confidence interval; CR, complete remission; CRc, composite CR; EFS, event-free survival; HR, hazard ratio; ITF, induction treatment failure. |
|||
|
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content




