All content on this site is intended for healthcare professionals only. By acknowledging this message and accessing the information on this website you are confirming that you are a Healthcare Professional. If you are a patient or carer, please visit Know AML.
The aml Hub website uses a third-party service provided by Google that dynamically translates web content. Translations are machine generated, so may not be an exact or complete translation, and the aml Hub cannot guarantee the accuracy of translated content. The aml and its employees will not be liable for any direct, indirect, or consequential damages (even if foreseeable) resulting from use of the Google Translate feature. For further support with Google Translate, visit Google Translate Help.
The AML Hub is an independent medical education platform, sponsored by Daiichi Sankyo, Johnson & Johnson, Syndax, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Kura Oncology, AbbVie, and has been supported through an educational grant from the Hippocrate Conference Institute, an association of the Servier Group.
Funders are allowed no direct influence on our content. The levels of sponsorship listed are reflective of the amount of funding given. View funders.
Now you can support HCPs in making informed decisions for their patients
Your contribution helps us continuously deliver expertly curated content to HCPs worldwide. You will also have the opportunity to make a content suggestion for consideration and receive updates on the impact contributions are making to our content.
Find out more
Create an account and access these new features:
Bookmark content to read later
Select your specific areas of interest
View AML content recommended for you
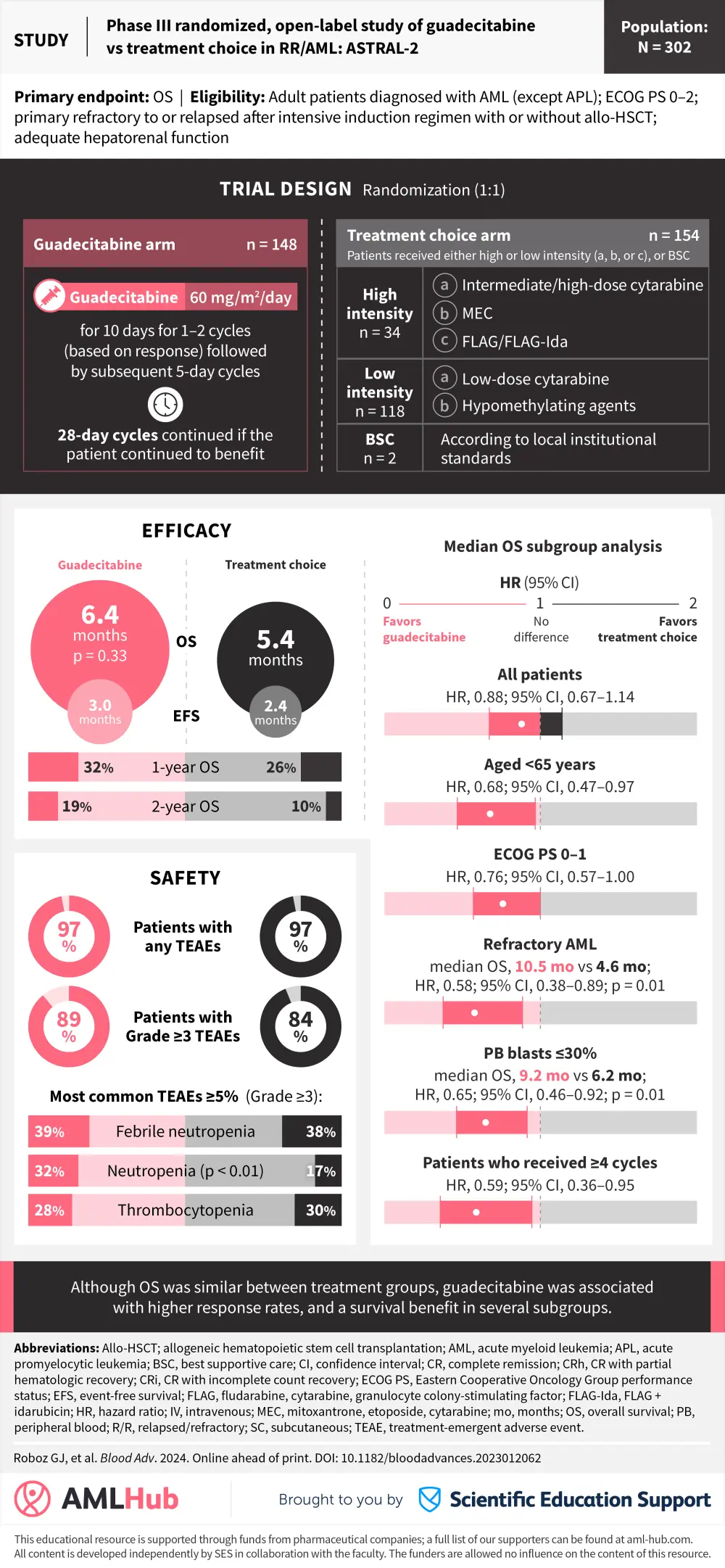
Visual abstract | Phase III randomized, open-label study of guadecitabine vs treatment choice in R/R AML: ASTRAL-2
The AML Hub is pleased to present a visual abstract summarizing results from the phase III ASTRAL-2 trial (NCT02920008) assessing guadecitabine, a next-generation hypomethylating agent vs standard-of-care treatment in patients with relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Results from this trial were published by Roboz et al.1 in Blood Advances.
Guadecitabine was associated with a higher rate of clinical response, and while overall survival was not improved, a survival benefit was observed in several prespecified subgroups.1.
References
Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statements:
The content was clear and easy to understand
The content addressed the learning objectives
The content was relevant to my practice
I will change my clinical practice as a result of this content




